Biology 441, Spring 2013: Lecture notes for January 30
Embryonic Induction Discovered by Hans Spemann & Hilde Proschöld
Transplantation of dorsal lip of the blastopore of salamander embryosPut into the blastocoel of another salamander embryo
Still unknown chemical signals from the grafted pre-notochord and pre-somite mesoderm stimulate change in differentiated fates of nearby somatic ectoderm so that it forms a second neural tube
Also, nearby lateral plate mesoderm converts to forming somites, etc.
Proschöld dies from stove fire soon after this discovery
Spemann becomes even more famous
Spemann wins Nobel Prize for discovering induction
Many more examples of induction are discovered
(tissues signal change in differentiation of nearby cells)
Subdivision of embryos into parts
*Blastula stage blastoderm (in birds) blastocyst (in mammals)*Gastrulation: subdivision of the developing embryo into 3 primary germ layers
Ectoderm is mechanically subdivided into three subdivision by the neurulation process
-
Neural tube ectoderm forms nervous system
Somatic ectoderm forms the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) & "placodes"
Neural crest ectoderm forms sensory nerves, autonomic nerves, pigment cells etc.
-
{Facial Skeleton is also formed by neural crest! which is strange}
The lining of the mouth is stomodeal ectoderm
made of cells from the stomodeum invagination
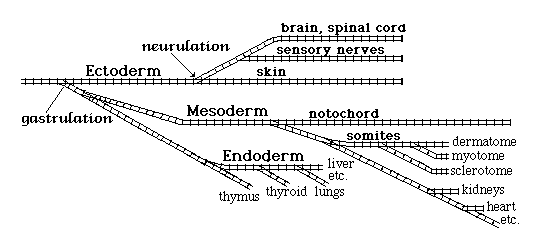
Mesoderm subdivides into:
-
Notochord
Somites
Intermediate mesoderm
Lateral Plate mesoderm
- Each somite subdivides into
-
Sclerotome (the cells of which will differentiate into cartilage and bone)
Myotome (whose cells will differentiate into skeletal muscles)
Dermatome (the cells of which will become the inner layer of skin, the dermis)
- 3 pairs of kidneys
male sex ducts
- Coelom
Heart
Uterus, and female sex ducts
-
pharnyx
Esophagus, stomach (the lining) which is surrounded by lateral plate mesoderm
Intestine (lining) which is surrounded by lateral plate mesoderm
liver
pancreas
lungs
thyroid gland
salivary glands (although some salivary glands are stomodeal ectoderm)
cloaca (which only in mammals gets subdivided into the following)
-
bladder
rectum