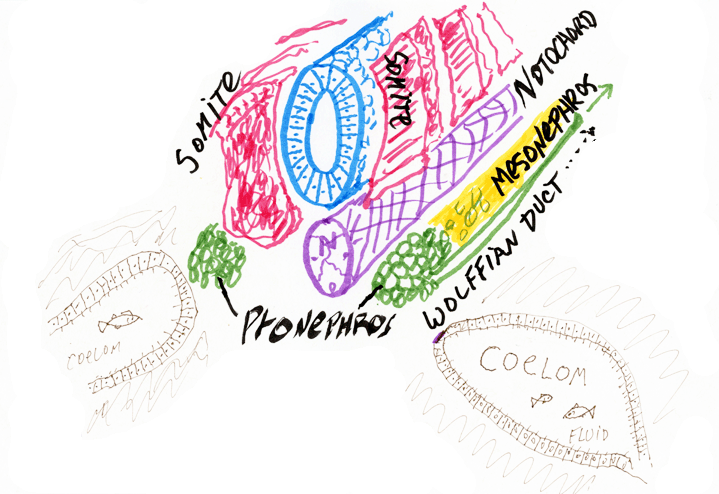
Lecture notes for Friday, February 8

Ectoderm
subdivides by folding, to form 3 subdivisions: underlined belowNeural Tube Ectoderm: Which itself subdivides to form the following:
-
Brain
Spinal cord
Motor nerves (one segmental motor nerve per somite).
Preganglionic Autonomic Nerves
Neural Retina
Pigmented Retina
Neural Crest Ectoderm:Which differentiates into many diverse cell types...
-
Sensory nerves, dorsal root ganglia (one per somite)
Postganglionic autonomic nerves
Melanocytes, and other mesenchymal pigment cells
Schwann Cells (but not oligodendrocytes)
Facial Skeleton (cell types that would be mesodermal in any other part of the body!)
Somatic Ectoderm: most of which becomes epidermis
-
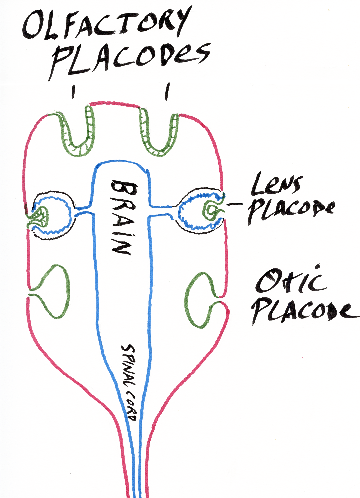
Some parts in the head become placodes:
A pair of olfactory placodes become nerves of the nose.
A pair of lens placodes become the lenses of the eyes.
A pair of otic placodes become the inner ear (semi-circular canals, cochlea, etc.).
In fish and amphibians, the lateral line system develops from placodes.
The inner ear uses neuromast cells to detect sound, gravity & water flow.
The lateral line system also uses neuromast cells to detect flow.

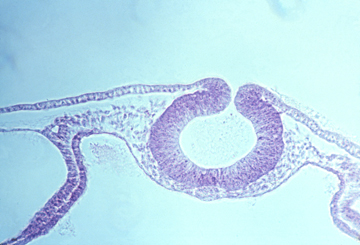
Section through chick embryo pharyngeal region
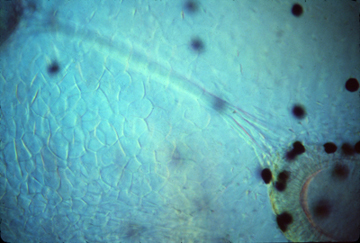
Olfactory nerve and placodes in a living Xenopus tadpole
Neuromast cells, right above here
Semi-circular canals in the same living tadpole
Otoliths in the same tadpole
These granules of calcium carbonate are embedded in a gel,
and detect which way is down, by pressure on neuromast cells.
Eyes

Histological section through embryonic chick eye
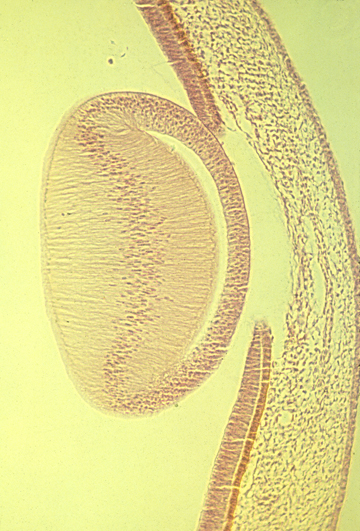
lens

Lens of a mammal eye:
Each cell is extremely long, extending from the posterior
side of the lens, almost all the way to the front
Eye cup with lens
pigment cells in a tadpole
Stomodeum and Digestive Tract
The most anterior end of the digestive tract is formed by an infolding of the ectoderm called the stomodeum.
The mouth:
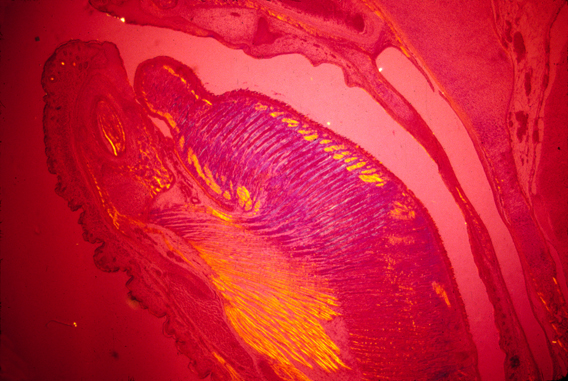
mouse tongue seen with polarized light
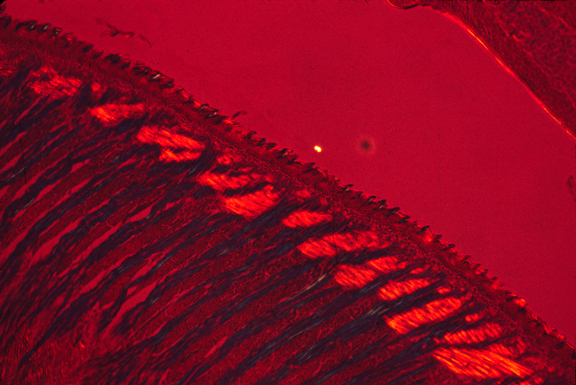
higher magnification showing orientation of muscles in perpendicular directions
Teeth
The outer layer of teeth (Ameloblasts --> Enamel)

tooth rudiments
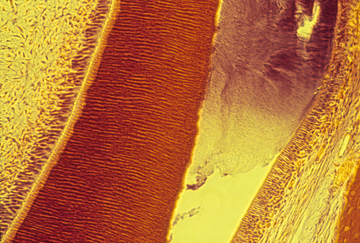
dentin and enamel
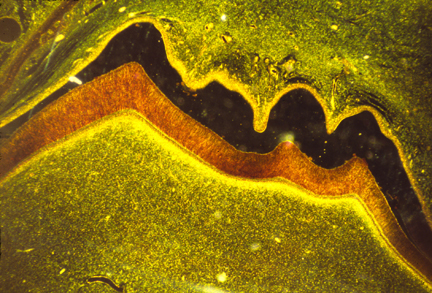
section of a molar
The dark area is empty space, where the enamel had been but broke off
during preparation of the slide. The orange area is the dentin.
pharyngeal pouches:
-
First Pharyngeal Pouch --> Eustachian Tubes
In case you were wondering, the Eustachian tube is named for Bartolomeo Eustachia, a sixteenth-century Italian anatomist 16th century Italian anatomist. This question came up in the lecture, but will not be asked on any exam.
Second Pharyngeal Pouch --> Tonsils
Third Pharyngeal Pouch --> Thymus and Parathyroid Gland
Fourth Pharyngeal Pouch --> Thymus and Parathyroid Gland
A question that might show up on an exam: what would happen if the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches did not develop properly?
Palatal shelves (which are only in mammals, not birds, not reptiles,
not amphibia or fish) separate the oral cavity from the nasal cavity, very much
like a pair of doors closing.
(When the palatal shelves don't fuse, the result is a birth defect called "Cleft Palate")
One of the 3 pairs of salivary glands and the anterior pituitary gland are stomodeal ectoderm. The rest of the digestive tract develops from endoderm, which will be covered in a later lecture.