February 26 lecture

Ectoderm
subdivides by folding, to form 3 subdivisions: underlined belowNeural Tube Ectoderm: Which itself subdivides to form the following.
-
Brain
Spinal cord
Motor nerves (one segmental motor nerve per somite).
Preganglionic Autonomic Nerves
Neural Retina
Pigmented Retina
Neural Crest Ectoderm:Which differentiates into many diverse cell types..
-
Sensory nerves, dorsal root ganglia (one per somite)..
Postganglionic autonomic nerves
Melanocytes, and other mesenchymal pigment cells.
Schwann Cells (but not oligodendrocytes).
Facial Skeleton (Cell types that would be mesodermal in any other part of the body!).
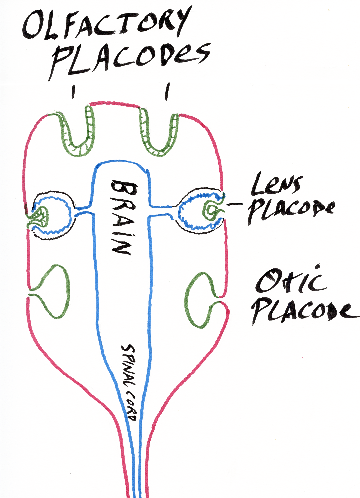
Somatic Ectoderm: most of which becomes epidermis
-
Some parts in the head become placodes
A pair of olfactory placodes become nerves of nose
A pair of lens placodes become the lenses of the eyes
A pair of otic placodes become the inner ear (semi-circular canals, cochlea, etc.)
In fish and amphibians, the lateral line system develops from placodes.
The inner ear uses neuromast cells to detect sound, gravity & water flow; The lateral line system also uses neuromast cells to detect flow.
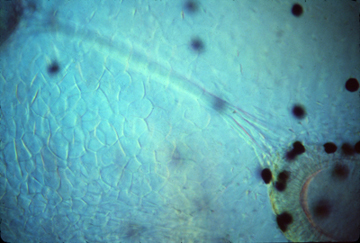


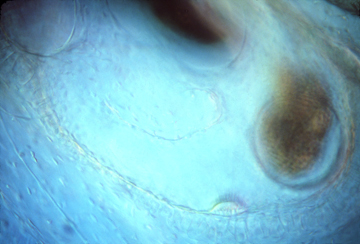
Neuromast cells, right above here
Semi-Circular Canals in a living Xenopus tadpole
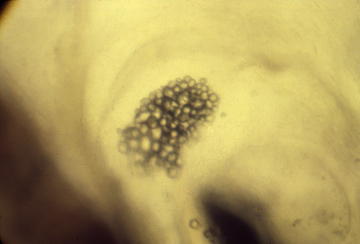
Otoliths in the same living Xenopus tadpole
These granules of calcium carbonate are embedded in a gel,
and detect which way is down, by pressure on neuromast cells.
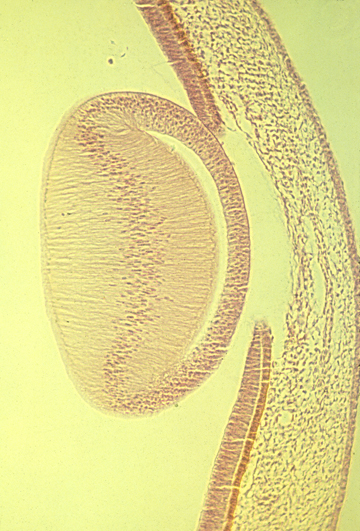

Lens of a mammal eye:
Each cell is extremely long, extending from the posterior
side of the lens, almost all the way to the front
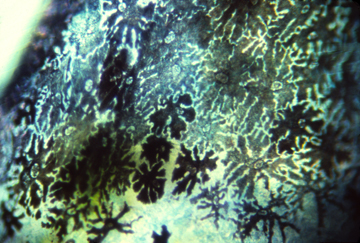
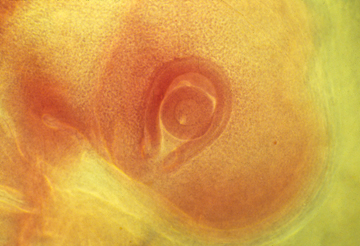
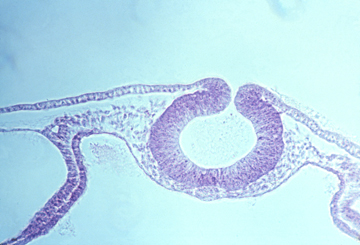
Eye cup with lens





video: axons in culture
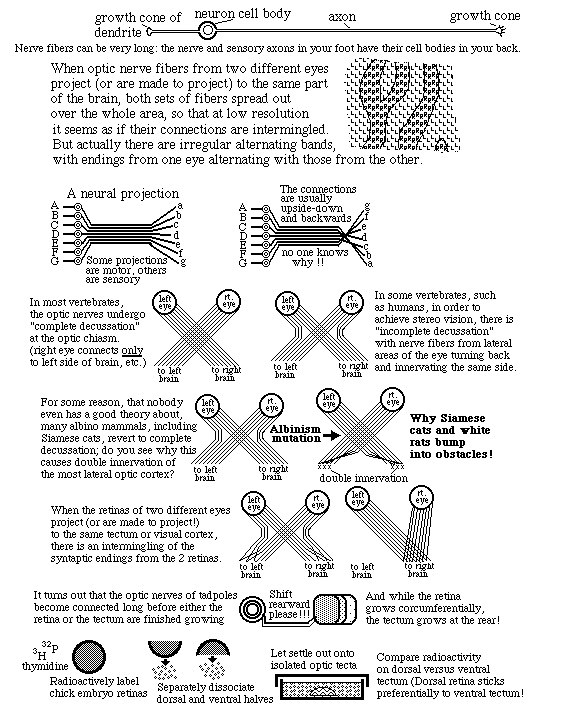
Retino-Tectal Projection
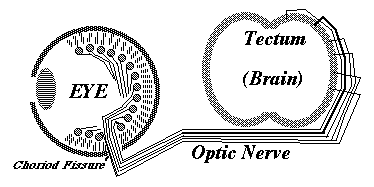

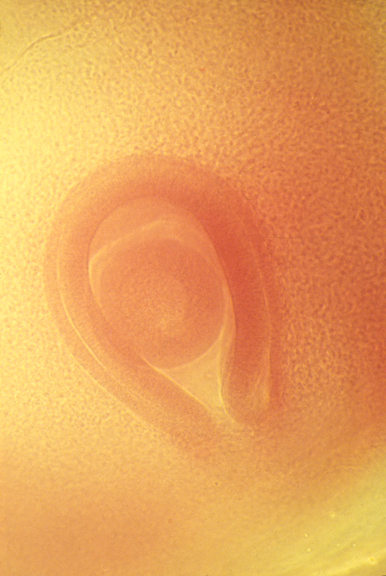
Embryonic eyeball, with retina surrounding it.
The groove is the location of the optic nerve.

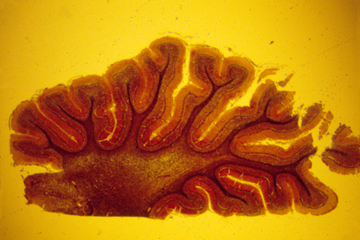
Cross-section of developing retina

Cross-section of optic nerve