Teratomas and neuroblastomas are relatively rare.
Benign tumors are not (yet!) invasive, but may become so.
Metastasis is transfer of cancer cells from one part of the body to another by breaking free into the lymph or blood (or coelom, or rarely, urine!)
Once cancer cells have begun to metastasize, then it is very much less possible to remove them all surgically.
(Thus, the great importance of early detection).
[Except for lymphoma, etc. which are metastatic very early]
-------------------------------------
Causes of Cancer
The great majority (>95%) of human cancers are caused by somatic mutations in a few specific genes (called "Oncogenes").
In many other species, large fractions of cancers are caused by communicable viruses. (Examples include cats and turkeys.)
This department gives a very good course specifically about oncogenes and how they cause cancer.
Several sexually transmitted papilloma viruses cause cervical cancer in women. A vaccine has been developed which inhibits infection by these cancer-causing papilloma viruses.
-------------------------------------
Some specific examples of oncogenes.
(About which you can learn much more in this department's course "The Biology of Cancer")sis: Codes for a form of PDGF (Platelet Derived Growth Factor). PDGF normally serves as a cell-to-cell signal, secreted by platelets and diffusing to other cells such as fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells, which it stimulates to grow and crawl about. If a cell produces its own form of PDGF, it behaves as if it were being constantly exposed to high concentrations of external PDGF; in other words, it stimulates its own growth and locomotion without limit. This is called autocrine stimulation. It is thought that the sis protein binds to the PDGF receptor proteins while these receptors are in the cytoplasm (prior to their insertion into the plasma membrane where their normal interaction with PDGF would have occurred).
erbB: Codes for an abnormal version of the membrane receptor for the extracellular protein called epidermal growth factor. This form of the receptor behaves as if it were constantly bound to molecules of its growth factor, thus constantly sending a false signal stimulating cell growth. A similar oncogene, called erbB-2 seems (based on its base sequence) to code for a receptor for some other (still undiscovered) growth factor. It is found in amplified form in about one fourth of all human breast and ovarian cancers!
ras: The function of its normal equivalent protein is to relay and amplify stimulatory signals, such as those from growth factor receptors. It binds a molecule of GTP whenever it is itself stimulated. It then relays stimulatory signals and continues to do so until its GTP is hydrolysed to GDP. Certain specific amino acid substitutions eliminate this protein's ability to hydrolyze bound GTP, however, so that it remains permanently in its "on" state, constantly "relaying" non-existent signals for the cell to grow and divide. Such mutations of this one oncogene are believed to be responsible for no fewer than one fifth of all human cancers, including up to half of colon carcinomas, and 90% of cancers of the pancreas! (Although note that several different ras genes are known.) Out of 25 average people, ras will kill one of them!
src: Codes for a protein that spontaneously becomes concentrated on the inside surface of the plasma membrane, especially at the sites of cell-substratum adhesion. This protein is an enzyme (a tyrosine kinase) whose effect is to catalyze the covalent bonding of phosphate groups onto the hydroxyl group of tyrosine amino acid residues of proteins. The proteins phosphorylated by the src protein include some which participate in the mechanical linkage between the actin cytoskeleton and materials to which the outside surface of the plasma membrane attaches; these changes may thus be responsible for weakening the cell's adhesiveness. Recent work in Patricia Maness' laboratory in the UNC Biochemistry Department indicates that the normal form of the gene functions in the chemotactic guidance of nerve growth cones. The src protein was the first tyrosine kinase to be discovered. Since all previously discovered kinases (there are many of them in the cell) had catalyzed the bonding of phosphates to the hydroxyl groups of serines and threonines, it was first assumed that phosphorylation of tyrosines was peculiar to cancer cells. But many normal tyrosine kinases have subsequently been found.
myc: Codes for a nuclear protein whose normal function seems to be as some kind of a transcription factor promoting cell growth. For example, when a normal cell is stimulated to grow and divide (for example, by exposure to PDGF), then the c-myc gene product (protein) temporarily increases in concentration; conversely, this gene normally becomes inactive in non-mitotic cell types. Many human cancers have been shown to have undergone amplification of the c-myc gene (often about 10 copies of the gene); this includes many cases of leukemia and about 30% of lung cancers of the highly lethal "small cell" type and breast cancers. The progression of cancerous cells to ever more and more aggressive states is frequently traceable to further amplification of the myc gene.
bcl-2: This name stands for B cell lymphoma and the protein for which this gene codes seems to have the normal function of inhibiting the spontaneous death of B-lymphocytes. In order that the total number of B cells in your body does not continue to increase without limit (because of constant exposure to different antigens) it is essential that the great majority of B-cells self-destruct. This self-destruction phenomenon ("apoptosis") will be discussed more fully below. When too much bcl-2 protein is produced in a given B cell, this blocks the self-destruction. Trans-genic mice with duplications of the bcl-2 gene accumulate abnormal concentrations of lymphocytes, among other abnormalities. Many human lymphomas result from promoter or enhancer sequences of the antibody genes (on the 14th chromosome) accidentally becoming spliced to the site on the 18th chromosome where the bcl-2 gene is located; whenever these B cells "try" to make antibody molecules, what they make instead is lots of the bcl-2 protein. These cells therefore accumulate to form a slow-growing lymphoma (which is always fatal, although not usually until one of the bcl-transformed clones has subsequently also been transformed by an over-activity of the myc oncogene). Prior to this they grow slowly, making it especially paradoxical that these lymphomas can be caused to shrink almost to nothing by the use of growth-poisoning chemotherapeutic drugs.
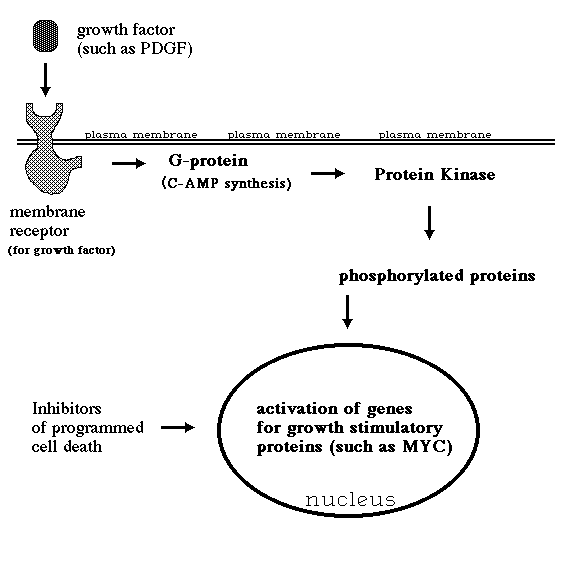
* Note that most of the oncogenes listed above are part of a "chain of command" by which external signals, especially protein growth factors, normally stimulate cell growth and division. A typical sequence of events would be for a (A) growth factor molecule to diffuse up to a cell's outer surface, then (B) bind to a membrane protein that serves as a specific receptor for that growth factor, with the conformation (C) or other properties of this receptor being changed by the binding, thereby causing either the activation of a cytoplasmic enzyme (that might be a protein kinase or ), or (D) the activation of a g-protein (such as the c-ras protein) that would then (E) activate a protein kinase, which would phosphorylate various cytoplasmic proteins, including some involved in cell adhesion, and would also stimulate increased transcription and translation of (F) genes for certain transcription factors such as c-myc. Paradoxically, myc also tends to stimulate apoptosis (G), unless counteracted by other gene products such as bcl-2.
Cancer cells from actual patients usually contain over-active versions of several different oncogenes, not infrequently 3 or 4 or more. Typically, there is one that acts at the nuclear level (such as myc) and one or more (such as ras or src) that act at the cytoplasmic level. For several years (between about 1982-86) it was confidently believed that cancer wouldn't occur unless there were at least two, and that one of the two had to be cytoplasmic in its action (like sis, erb, ras or src) and that the other had to act at the nuclear level (like myc). But this is no longer believed.
At current rates in the USA, 25% of you will get cancer.
Four-fifths of this 25% will die of their cancer.
That's 20 people out of every one hundred.
-------------------------------------
Abnormalities of Cancer Cells
1) Glucose uptake is much higher than normal in most cancer cells.Related to this is an abnormally (very) large secretion of lactic acid, and abnormally low amounts of ATP production by mitochondria. This set of inter-related abnormalities was discovered around 1930 by Warburg, who had won the Nobel Prize for previous discoveries, and is one of two (unrelated) phenomena both called "The Warburg Effect". Excess glucose uptake into cancer cells is the reason why PET scans can detect cancer, and reliably distinguish cancer cells from normal cells. I have had several PET scans myself, and they accurately mapped the tumors. They cost about three thousand dollars per scan.
The biochemical cause of these phenomena remains unknown, and very little research has been done on it, because it doesn't fit in with oncogene research. The best English language textbook on cancer biology doesn't even mention the Warburg effect. Almost no research has been done about how to kill cancer cells based on either their anaerobic metabolism, or the excess uptake of glucose. (Despite very large amounts of research on how to use the phenomenon to map tumors).
2) Magnetic Resonance Images of cancer cells are visibly different than normal tissues.
This was the subject of the first research paper about MRI.
Nobody ever discovered the reason why cancer cells' MRI images are abnormal.
Almost no research has been done on the subject.
3) The acto-myosin cytoskeleton of cancer cells is disorganized, and they exert much weaker traction forces as they crawl.
4) Cancer cells can crawl onto less adhesive substrata,
from more adhesive substrata. This is a loss of haptotaxis.
It was discovered by Prof. Barbara Danowski, as part of her PhD research
in this department. She invented the experiment herself. She then did
important research at the University of Pennsylvania, and is now
Professor and Chair of Biology at Union College in New York.
I had never considered the possibility, until she proved it.
5) Defective cell-cycle checkpoint controls.
For example, cancer cells tend to go ahead and copy DNA, even if it is damaged.
Normal cells would delay starting to copy their DNA until
damage to it has been repaired.
6) Excessive inhibition of apoptosis.
In particular, 95% of cases of the "follicular" kind of Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
are caused by a breakage and incorrect re-joining of the 14th chromosome
and the 18th chromosome, in such a way that the promoter region of the
antibody heavy chain gene is next to a gene named bcl-2. This stands for
b-cell lymphoma two, because it was the second lymphoma-causing gene to be
discovered by looking for chromosome translocations in cancerous lymphocytes
of human patients. Nematodes have a gene almost identical to human bcl-2.
It is needed to inhibit programmed cell death, both in vertebrates and in
nematodes (and probably all animals). Experimenters have even spliced the
human DNA sequence for bcl-2 into nematodes, in place of the nematode's own
gene. The human gene works fine in nematode embryonic development.
When a human b-lymphocyte has this particular chromosome translocation, it makes bcl-2 protein instead of antibody, and can't undergo programmed cell death. Although such lymphocytes don't grow or divide any faster than normal lymphocytes, they do accumulate without limit. Eventually, they displace your normal lymphocytes and fill up your bone marrow, until you become anemic, can't make antibodies etc. and die.
Ironically, the treatment is often a chemical designed to kill fast-growing cells by damaging their DNA. It was assumed the cancerous lymphocytes must be growing too fast, and that cross-linking their DNA would selectively kill the fastest growing lymphocytes.(That, itself, isn't very logical. Why should it kill a cell to prevent it from doing something abnormal? If they grew slower than normal, would you expect to be able to kill them by speeding them up?)
The lecture on Friday, April 12, stopped here. We will continue on Monday.
-------------------------------------
Consider the following hypothesis about how chemotherapy really works:
When DNA is damaged by radiation or a drug like cyclophosphamide,
non-cancerous cells detect the damage and slow down their growth,
halting at a check-point until the damaged DNA has been fixed.
The cancerous cells, however, because their check-point controls are broken,
continue to copy DNA and undergo mitosis. This failure to stop is really
what kills them. This is sort of the opposite of what had been assumed.
Cancer cells die because they can't stop, not because they grow too fast.
Any time a drug works, there must be some reason; but the true reason may
be very different than what the drug was designed to do.
7) Lack of anchorage dependence, the ability of cells to survive and continue dividing without being spread out on a solid substratum.
Cancer cells can grow and survive suspended in a gel. Non-cancerous cells will undergo programmed cell death if you culture them on an area of substratum that is smaller than the area they normally occupy when attached to a Petri dish. Nicholas Maroudas and Donald Ingber have done the best research on this.
8) Increased secretion of proteolytic enzymes
9) Loss of differentiated characteristics ("tumor progression")
-------------------------------------
Diagnosis of cancer cells by shape and behavior
Cancer cells are usually somewhat abnormal in shape and structure, as seen under the microscope in histological sections.
The well known Pap test depends on this fact, although it uses tissue scrapings rather than sections. It is not unusual for cancer operations to begin with the surgeons cutting out a small chunk of the tumor, then sending it down the hall to the histology lab for quick fixation, sectioning, staining and examination by a skilled pathologist.
Just by looking at the shapes of the cells and particularly the shapes of the nuclei, the pathologist is supposed to be able to tell whether the tissue is malignant or not.
Often there are 3 options: (1) stitch up the incision, because the tissue is benign; (2) continue with the operation and try to remove as much as possible of the tumor, because it is malignant, or; (3) stitch up the incision, because the cells are so extremely malignant that experience has proven that there is no hope from surgery.
The patient, lying there waiting, and the family members waiting down the hall, might wonder what cellular differences the pathologist is looking for.
Books have been written summarizing the criteria used for this purpose. The quotation below is from "The Cytological Diagnosis of Cancer" by Ruth M. Graham, 3rd. edition Saunders, Philadelphia. (Health Sciences Library QZ 241 G 741 1972) page 379:
"Whether a cell is malignant or benign is determined by its nucleus; what type of malignant or benign cell it is determined by the cytoplasm."
"In examining a cell, the microscopist should first look at the nucleus and decide whether it is benign or malignant."
"The first feature to look for is the orderly arrangement of the chromatin. Are the chromatin particles of equal size? Are they distributed evenly throughout the entire nucleus? Is the nuclear border smooth and even in thickness? Does each part of the nucleus resemble every other part? If, in the mind's eye, the nucleus were bisected, would the two halves be mirror images of one another? If the answers to these questions are "yes", then one can be sure the nucleus is benign.
On the other hand, if the answers to these questions are "no"; if the chromatin particles differ in size; if they are distributed unequally at the nuclear border, and in the bisected nucleus no part is a mirror image of any other part, then one can be sure that the nucleus is malignant. "
Note that these criteria are entirely empirical (arrived at purely by experience, not based on any theory or other reason for expecting them). Cells with one set of properties always turned out to be malignant in their future behavior (if not removed), while cells with the other sets of properties always turned out to be benign. Mistakes are sometimes made, even mistakes in the direction of diagnosing malignant cells as benign; but given the amounts of money involved in malpractice lawsuits, it seems noteworthy to me that the quotes above could be so general and sweeping. It is almost as if the weather could be accurately predicted from the shapes of clouds, but no one had bothered to find out the physical causation relating the shapes of today's clouds to the occurrence of tomorrow's storms! There has been little or no research into the question of how cell and nuclear shape is related to oncogene function.
The histological organization of cancer cells is also abnormal; the cells' arrangements as "sloppy": they are irregular in shape, sizes and relative positions, as well as slightly out of alignment. What does this imply about the mechanisms that control cell shape, size, relative position, alignment, etc.? Would you prefer to say that the cancerous state interferes with these mechanisms? Or would you say that malignancy results from the disruption or failure of these mechanisms? Your new ideas might really help treatment.

-------------------------------------
Examples of Current Methods of Cancer Chemotherapy:"Nitrogen mustards" such as cyclophosphamide (chemical relatives of "mustard" war gasses used in World War I) damage DNA, and tend to kill faster-growing cells."Spindle poisons" such as vinblastine, which bind selectively to tubulin and block formation of the mitotic spindle. Monoclonal antibodies, with binding sites that specifically fit cell surface proteins that happen to be more numerous on a given patient's cancer cells (for example "Herceptin") or that attack all the patient's cells of the same differentiated cell type as that person's cancer. For example, "Rituxan" (rituximab) attacks ALL of a person's B-lymphocytes. Monoclonal antibodies can also be made that are specific for an individual person's B-cell lymphoma but they are regarded as "prohibitively expensive" and are not being widely used. See this quote from a widely used immunology textbook. Notice the lack of specificity of any of these categories of treatments. None of them is even designed to kill only cancer cells. Also notice that monoclonal antibodies aren't really drugs, but are medically equivalent to the passive immunity of anti-snake bite injections. They were invented by British government researchers in Cambridge, England. More hopeful developments: A researcher synthesized a chemical that selectively blocks a certain ATPase protein made only by lymphoma cells of a certain sub-type. This is a "fusion protein" coded for by DNA sequences that were originally on different chromosomes, but two chromosomes often break and rejoin at the wrong places, creating the "Philadelphia Chromosome", and coding for an over-active kinase that stimulates cell growth and inhibits apoptosis. The synthetic chemical drug (called Gleevec) has enough specificity for this fusion protein enzyme to kill 99% + of many patients' cancerous lymphocytes. There were many optimistic news reports about this drug in the past few years. Nevertheless, I think you and I should be more curious about: #1 Why it kills cells to block activity of this abnormal enzyme? (that they aren't supposed to have, anyway!) #2 Considering that cells have about a thousand normal ATPases, what are some possible reasons why a poison can inhibit only one? Possible explanations are (1) maybe this abnormal enzyme is keeping cells from killing themselves by apoptosis, so weakening it lets them die; and (2) maybe the inhibitor also inhibits many or all of the other, normal ATPases, but that doesn't hurt normal cells unless their apoptotic machinery were already activated. But #3, these paradoxical aspects were never mentioned in news stories. Like almost everyone else, I expected that when the causes of cancer were completely understood at the molecular level then we would see how to cure it. So far, however, this information (about oncogenes, etc.) has not been useful for curing patients. What is needed are methods to kill just those cells in which oncogenes are over-active. Blocking the activity of oncogenes doesn't really do you any good. You have to kill just those cells in which the oncogenes are causing cancer.
|
|
You have to kill just those cells in which the oncogenes are causing cancer. You have to kill just those cells in which the oncogenes are causing cancer. You have to kill just those cells in which the oncogenes are causing cancer. You have to kill just those cells in which the oncogenes are causing cancer.
You have to kill just those cells in which... don't forget.
|
|
-------------------------------------
How you might invent a new cure for cancer!Always keep in mind, the key problem is specificity.
|
| SOMETHING IN THIS COLUMN | NEEDS TO BE INDUCED BY
SOMETHING IN THIS COLUMN | Initiation of Apoptosis | Abnormalities of cancer cells | i) Caspase enzyme activation | a) Over-activity of certain kinases | ii) Non-self, viral-like peptides | b) Excessive phosphorylation of certain proteins (held by type I histocompatibility antigens) |
iii) Fas/Fas ligand stimulation | c) Mutated GTPases, unable to hydrolyse GTP | iv) Other damage to cells? | d) Anaerobic metabolism e) Inability to halt at cycle checkpoints f) Lactic acid production g) Secretion of proteolytic enzymes h) Disrupted cytoplasmic actin i) Abnormal adhesions j) Less fibronectin secretion |